Rate Limits
For user actions that have a rate limit, like reblogging a given artwork, a rolling rate limit is stored in Redis for one or more duration periods.
Key structures
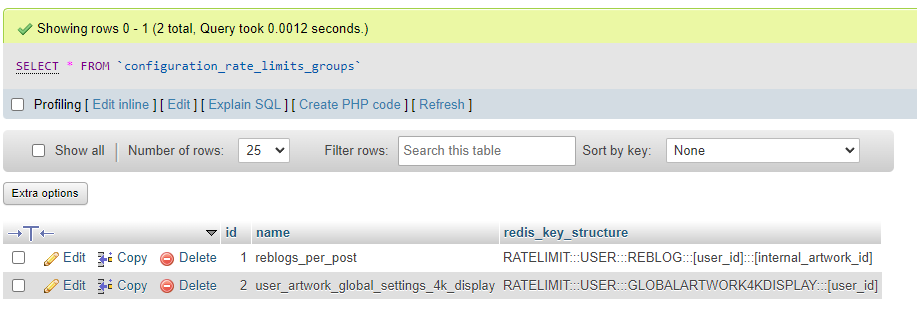
The structure for each rate limit's Redis key is kept in the configuration_rate_limits_groups database table. Each row represents one "action", such as reblogging an artwork. The configuration_rate_limits database table holds one or more rows per rate limit group, each of which corresponds to a duration and maximum value for the rate limit.
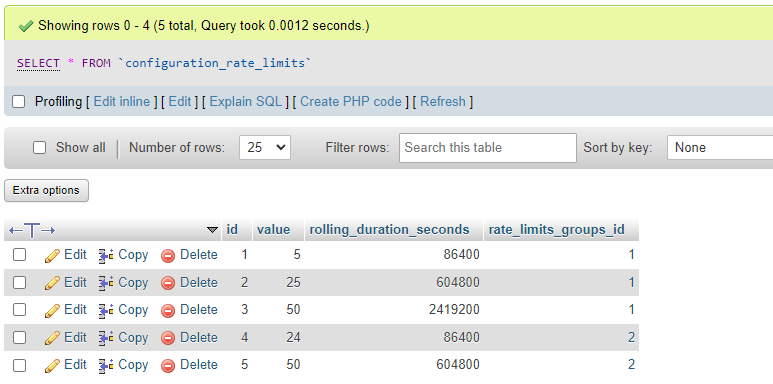
Example database configuration
Here, the reblog action has three separate rate limit periods: a maximum of five reblogs per day (value 5, rolling duration seconds 86000 = 1 day), 25 reblogs per week, and 50 per month. This prevents a user from aggressively unreblogging and reblogging a given artwork to manipulate the latest or following feeds.
Each rate limit in a group has a separate redis key, constructed by taking the main redis key structure for that group and adding ":::SECONDS" to it. For example, the rate limit with ID 1 above would be represented in Redis with the key "RATELIMIT:::USER:::REBLOG:::[user_id]:::[internal_artwork_id]:::86400", ensuring each limit in a given group has a unique key.
PHP classes
The Core\Redis\RateLimitManager.php class provides functions for checking if a rate limit has been exceeded, and incrementing the values for a rate limit. The Config\RateLimitsConfig.php class provides constants that correspond to the name field in the configuration_rate_limits_groups table that are used to query a given rate limit in Redis (the group list is cached in Redis to prevent unnecessary database calls).